Anaerobic biological treatment – No oxygen needed
Anaerobic treatment of wastewater is a biological process that decomposes organic matter in the absence of oxygen. This method depends on anaerobic microorganisms, particularly methanogenic bacteria, which thrive in oxygen-free environments.
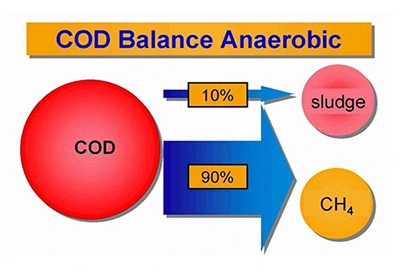
The anaerobic process effectively reduces most of the Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) in the wastewater by transforming it into biogas, which consists of Methane (CH4) and Carbon Dioxide (CO2), while maintaining low operational costs.
Why anaerobic treatment?
- Requires up to 90% less space compared to conventional systems.
- No aeration needed, leading to minimal energy consumption.
- Significant reduction in CO2 emissions.
- Up to 90% less excess sludge, eliminating disposal costs.
- Can handle high organic loads, suitable for industries generating highly polluted wastewater.
- Uses granular anaerobic sludge as seeding material for a quick and efficient commissioning process.
- Converts organic pollutants into biogas (a mix of methane and carbon dioxide), which can be captured and used as an energy source.

